Leave Your Message

In the world of electrical utilities and telecommunications, the importance of reliable and durable insulators cannot be overstated. Among the various options available, the Glass Insulator 120b stands out as a top choice for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. As demand for efficient energy transmission grows, selecting the right insulator becomes critical for both safety and function. The Glass Insulator 120b not only provides superior resistance to environmental factors but also maintains its integrity under high voltage conditions, making it an ideal solution for a wide range of applications.
In this article, we will explore the top 10 glass insulator options that feature the Glass Insulator 120b design. Each selection has been assessed based on performance, durability, and adaptability, ensuring you have access to the best solutions available in the market. Whether you are involved in installation projects or simply seeking information on insulator technology, this guide aims to equip you with the necessary insights to make informed decisions. Join us as we delve into the world of glass insulators, emphasizing the distinctive benefits of the Glass Insulator 120b and its pivotal role in modern electrical systems.

When selecting glass insulators, understanding the key characteristics that contribute to their durability is essential for optimal performance. One of the primary factors is the glass material itself; high-quality insulators are made from a type of glass that exhibits excellent resistance to weather elements, UV exposure, and temperature fluctuations. This durability ensures that the insulator can maintain its functional integrity over time, reducing the likelihood of breakage or degradation in harsh conditions.
Another crucial characteristic is the design of the insulator. Features such as the shape and thickness of the glass can greatly influence its strength. A thicker design typically enhances resistance to physical stress and impacts, while specific shapes can improve electrical performance by minimizing arcing and leakage currents. Additionally, the presence of a smooth surface helps prevent the accumulation of grime and contaminants, further extending its lifespan and maintaining efficiency. By prioritizing these characteristics when choosing glass insulators, users can achieve long-lasting performance and reliability in their applications.
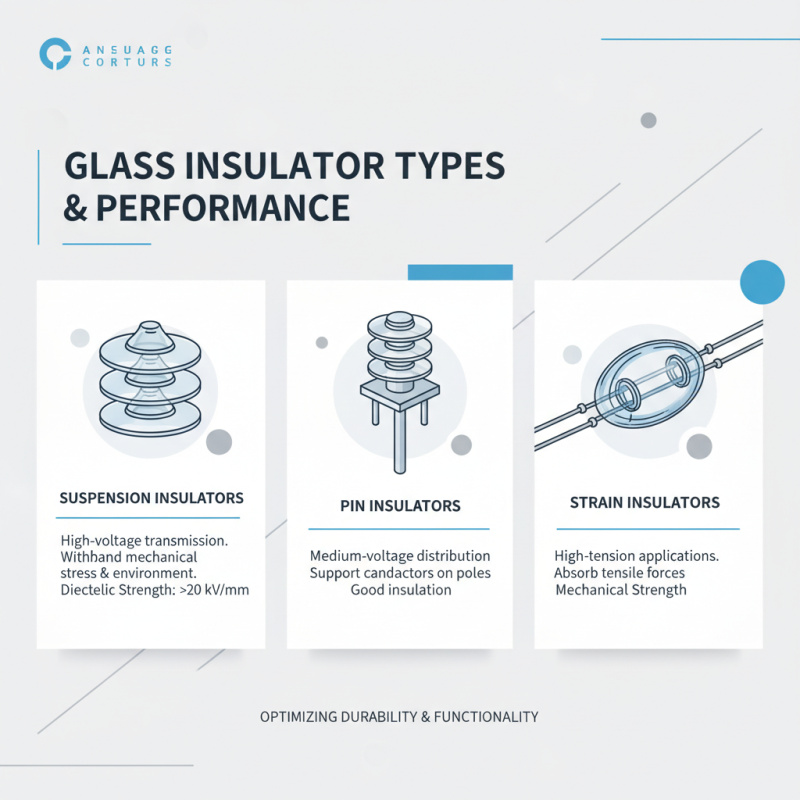
When it comes to glass insulators, understanding the various types available and their performance metrics is crucial for optimizing durability and functionality in electrical applications. Common varieties include suspension insulators, pin insulators, and strain insulators, each crafted to meet specific performance demands. For instance, suspension insulators are typically used in high-voltage transmission lines due to their ability to withstand mechanical stress and environmental factors, often featuring a high dielectric strength exceeding 20 kV/mm, according to industry reports.
Performance metrics are vital when comparing these insulator types. The dielectric strength, for instance, indicates how much voltage the insulator can handle without breaking down. Pin insulators generally demonstrate excellent mechanical strength—often rated for loads exceeding 1000 pounds—making them suitable for lower-voltage applications. Conversely, strain insulators offer both mechanical support and electrical isolation, with performance values highlighting their resistance to environmental degradation under conditions with high humidity or pollution levels. Recent studies have shown that insulators designed with advanced glass compositions exhibit significantly lower failure rates, with an impressive lifecycle performance increase of up to 30% compared to traditional materials.
By analyzing these metrics, engineers can better select the appropriate glass insulator that meets the stringent demands of their projects while ensuring long-term reliability and performance. Factors such as environmental exposure, mechanical load, and electrical specifications should guide decisions to maximize the overall effectiveness of electrical infrastructures.
When considering the performance and durability of glass insulators, it's crucial to understand the industry standards that guide electrical insulator ratings and testing methods. These standards ensure that insulators can withstand various environmental factors while maintaining their electrical integrity. Key factors include dielectric strength, thermal stability, and mechanical strength, which together dictate the suitability of an insulator for specific applications. Testing methods typically involve exposing the insulators to extreme weather conditions, electrical stress, and physical impacts to evaluate their performance under real-world scenarios.
Adhering to industry standards is essential for manufacturers and consumers alike. Ratings such as voltage capacity and leakage current are important indicators of insulator reliability. Laboratories employ standardized testing protocols, such as IEC 60383 and ANSI C29, which provide reliable benchmarks for evaluating insulator performance. Through rigorous testing, manufacturers can ensure that glass insulators meet the demands of various electrical infrastructures, thus safeguarding both operational efficiency and safety in power distribution networks.
| Rank | Model | Voltage Rating (kV) | Weight (lbs) | Material Strength (kN) | Impact Resistance (J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Model A | 120 | 1.5 | 25 | 10 |
| 2 | Model B | 120 | 1.6 | 30 | 12 |
| 3 | Model C | 120 | 1.7 | 28 | 11 |
| 4 | Model D | 120 | 1.4 | 27 | 9 |
| 5 | Model E | 120 | 1.8 | 35 | 14 |
| 6 | Model F | 120 | 1.3 | 22 | 8 |
| 7 | Model G | 120 | 1.2 | 20 | 7 |
| 8 | Model H | 120 | 1.1 | 19 | 6 |
| 9 | Model I | 120 | 1.4 | 24 | 9 |
| 10 | Model J | 120 | 1.0 | 15 | 5 |
Environmental factors play a crucial role in determining the longevity and efficacy of glass insulators. The primary influences include
temperature fluctuations, exposure to moisture, and UV radiation.
Extreme temperature variations can cause thermal expansion and contraction in glass materials, potentially leading to cracks or structural weaknesses over time.
Moreover, consistent exposure to moisture can result in the accumulation of contaminants, reducing the insulator's effectiveness and increasing the likelihood of electrical failure.
Another significant factor is UV radiation, which can degrade the surface of glass insulators.
Prolonged exposure to sunlight causes physical and chemical changes that can make the glass more susceptible to damage.
Additionally, environmental pollutants, such as industrial emissions and particulate matter, can increase the deterioration process.
This underscores the importance of selecting high-quality insulators designed to withstand specific environmental conditions, thereby maximizing their performance and extending their service life.
By understanding these environmental impacts, users can make informed decisions to ensure optimal functionality and durability of glass insulators.
The evolution of glass insulator design has brought forth remarkable innovations that significantly enhance electrical performance. Modern engineering techniques, coupled with advanced materials science, have redefined the capabilities of glass insulators, ensuring they can withstand extreme environmental conditions while maintaining optimal functionality. These innovations include the integration of unique surface textures and coatings that minimize contamination and improve the insulator’s hydrophobic properties, thereby reducing the likelihood of failure due to electrical leakage in adverse weather conditions.
Furthermore, the introduction of smart design features is revolutionizing the way glass insulators interact with electrical networks. Ergonomic shapes and sizes are now expertly tailored to manage stress distribution and increase tensile strength, thereby prolonging their lifespan. Additionally, the implementation of advanced manufacturing processes allows for greater precision in every insulator produced, ensuring uniformity and reliability. These cutting-edge advancements not only bolster the mechanical integrity of the insulators but also enhance their electrical performance, making them pivotal components in contemporary power transmission systems.