
Leave Your Message

The "Double Shed Glass Insulator" is an intriguing yet vital component in the realm of electrical transmission and distribution. These insulators serve a crucial purpose in maintaining the integrity and reliability of power lines, particularly in regions prone to severe weather conditions. A recent report by the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) indicates that insulator failure can lead to significant outages, resulting in economic losses estimated at billions of dollars annually. Consequently, the deployment of robust insulator solutions, such as the Double Shed Glass Insulator, is paramount for the resilience of electrical infrastructure.
Designed to withstand harsh environmental factors, the Double Shed Glass Insulator effectively mitigates the risks associated with contamination and moisture. Its unique double shed design enhances performance by providing superior shedding capabilities, which reduce pollution-related flashovers. According to a comprehensive analysis by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), glass insulators, particularly those featuring advanced designs like the double shed configuration, significantly outperform traditional porcelain insulators in longevity and reliability.
As the demand for electricity continues to rise globally, with the International Energy Agency (IEA) projecting that electricity consumption will expand by nearly 50% by 2040, the importance of reliable components like the Double Shed Glass Insulator cannot be overstated. By ensuring the safe and efficient transmission of electrical energy, these insulators play a critical role in supporting the evolving energy landscape and facilitating the transition towards sustainable power systems.
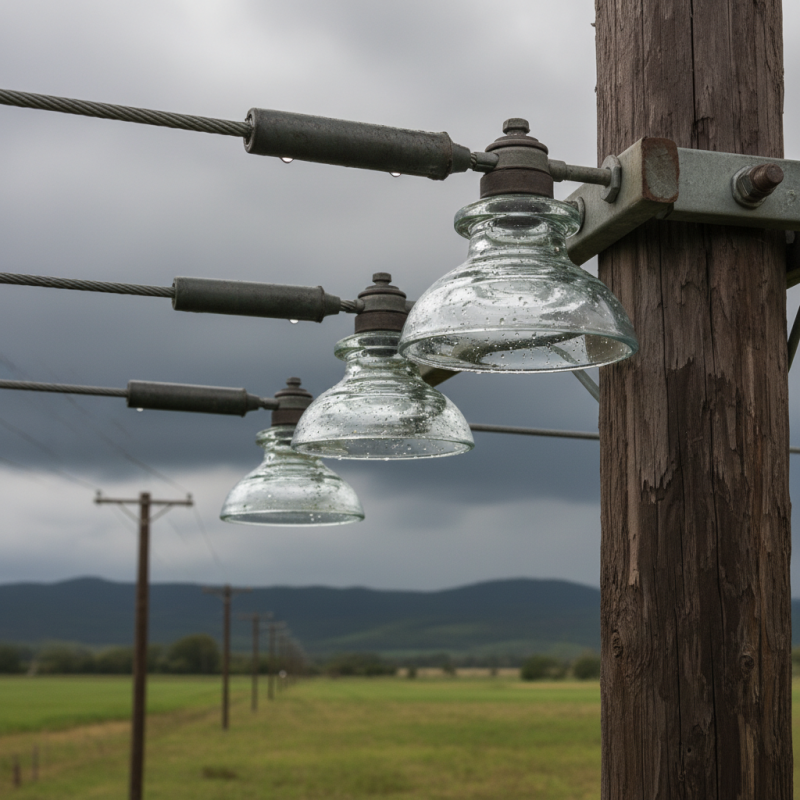

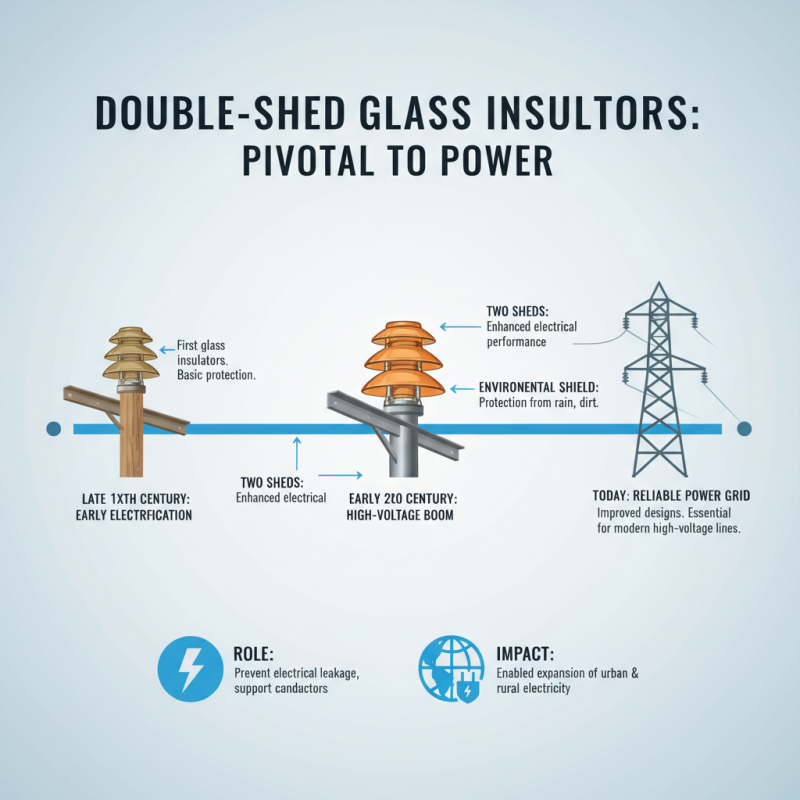
Double shed glass insulators have played a pivotal role in the evolution of electrical transmission systems. These devices, characterized by their two distinct sheds or skirts, were designed to enhance electrical performance and provide effective protection against environmental elements. The first known application of glass insulators dates back to the late 19th century, as electrification began to spread across urban and rural areas. Double shed insulators were introduced in response to the growing need for improved performance in high-voltage transmission lines.
Historically, the design innovation of the double shed insulator allowed for better voltage regulation and reduced the chances of electrical arcing. According to the Insulator Collectors Association, these insulators can handle voltages typically ranging upwards of 69 kV, demonstrating their robustness and reliability in harsh weather conditions. The dual-shed design promotes a longer electrical path, thereby minimizing leakage currents and improving insulation capabilities. Additionally, organizations like the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) emphasize that the use of double shed glass insulators contributes to enhanced safety standards and greater operational longevity, a crucial aspect for utility companies aiming to maintain efficient power distribution networks.
Double shed glass insulators are engineered with a unique construction designed to enhance their performance in electrical applications. The key feature of these insulators is their double shed design, which consists of two distinct sheds that extend outward from the main body. This design effectively increases the surface area and provides additional protection against environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and pollution. The sheds channel rainwater and dirt away from the insulator, minimizing the risk of electrical leakage and ensuring reliable performance over time.
Moreover, the manufacturing process of double shed glass insulators typically involves high-strength glass that can withstand extreme weather conditions and mechanical stress. This resilient material is crucial for maintaining the insulator's integrity, especially in outdoor settings where exposure to harsh elements is common. The transparent nature of glass also allows for easy visual inspection, enabling maintenance personnel to quickly assess the condition of the insulator. By combining these design features, double shed glass insulators effectively ensure safety and reliability in transmission and distribution systems.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | Typically made of glass for high dielectric strength. |
| Shed Design | Features two sheds to improve electrical performance and reduce pollution tracking. |
| Voltage Rating | Commonly rated for high voltage applications, often between 10 kV to 200 kV. |
| Configuration | Designed with a base that allows for easy mounting on poles. |
| Color | Typically clear or colored to enhance visibility and aesthetic appeal. |
| Mechanical Strength | Designed to withstand environmental stresses such as wind and ice loads. |
| Applications | Used in overhead power lines, substations, and telecommunications. |
| Maintenance | Usually requires minimal maintenance; cleaning may be needed in polluted environments. |
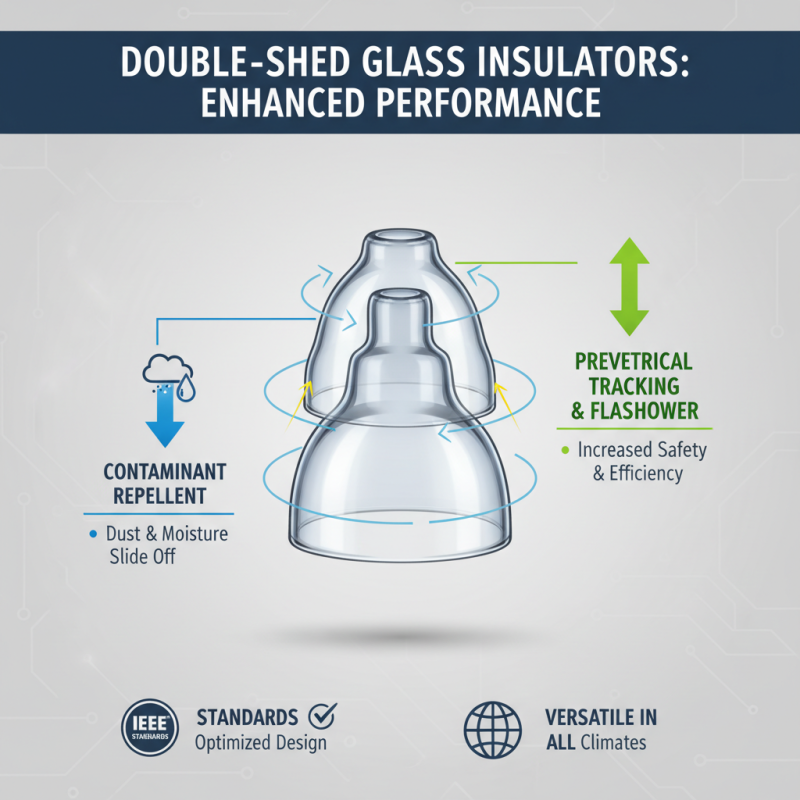
Double shed glass insulators play a crucial role in maintaining electrical systems' efficiency and safety, particularly in overhead transmission lines. Constructed with two distinct sheds, these insulators optimize their functionality by ensuring that contaminants, such as dust and moisture, slide off easily, thereby preventing electrical tracking and flashover. According to the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) standards, the design of double shed insulators allows for enhanced performance under various environmental conditions, which is critical for electrical infrastructure operating in diverse climates.
The operational mechanism of double shed glass insulators revolves around their ability to provide mechanical support and electrical insulation. The sheds create a longer path for electrical current, which helps in minimizing the chances of leakage. Research published by the National Electrical Safety Code highlights that insulator efficiency can significantly reduce system outages, with properly designed double shed insulators achieving failure rates less than 0.01% in optimal conditions. This is particularly relevant in high-voltage applications where reliability is paramount. The use of double shed insulators ensures that transmission lines maintain integrity over time, contributing to overall grid stability and reducing maintenance costs associated with insulator failure.
Double shed glass insulators play a crucial role in electrical systems by providing effective electrical insulation and mechanical support for overhead power lines. Their unique design, featuring two separate sheds or outward projections, helps to shed water and debris, minimizing the risk of electrical tracking and ensuring reliable operation in various environmental conditions. According to a report from the International Electrotechnical Commission, the use of glass insulators can significantly enhance the performance of transmission lines, particularly in areas with high pollution or frequent weather fluctuations.
In terms of applications, double shed glass insulators are commonly utilized in high-voltage transmission lines, where their superior insulating properties are essential for maintaining system integrity. The American Electric Power Research Institute noted that glass insulators offer low power loss and high resistance to aging, making them ideal for long-term use in critical infrastructure. Furthermore, the use of glass insulators minimizes maintenance costs over time, as they are less susceptible to damage compared to porcelain insulators, providing a reliable solution for utilities aiming to reduce operational expenses while ensuring safety and efficiency in energy delivery.
Double shed glass insulators are vital components used in high-voltage transmission systems, designed to support and insulate electrical conductors. Their structure, comprising two distinct shed sections, enhances the surface area, effectively mitigating the risk of electrical tracking and flashover caused by contaminants like dust and moisture. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the reliability of insulators in high-voltage lines is critical, with a failure rate decrease of about 30% observed in systems utilizing advanced glass insulator technology.
The benefits of double shed glass insulators are multifaceted. First, they boast excellent dielectric properties, enabling them to withstand high electrical stress while ensuring minimal energy loss. Their robust design increases their longevity and resistance to environmental stressors, thus reducing maintenance costs. Industry data suggests that the lifespan of modern glass insulators can extend up to 50 years, significantly outperforming traditional porcelain counterparts. Furthermore, their transparency to UV light minimizes degradation from sunlight exposure, thereby maintaining performance throughout their operational life. With these advantages, double shed glass insulators are increasingly favored in applications where reliability and efficiency are paramount, as confirmed by the latest findings from the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI).





