
Leave Your Message

When it comes to designing and maintaining an efficient electrical system, choosing the right Isolator High Voltage is crucial for ensuring safety and reliability. Isolators serve as essential components that allow for the disconnection of electrical circuits when maintenance or repair is necessary, thus preventing accidents and enhancing operational efficiency. With a variety of options available, selecting the most suitable isolator requires careful consideration of several key factors including voltage ratings, environmental conditions, and installation requirements.
Understanding the different types of Isolator High Voltage and their applications can significantly impact the performance of your electrical system. It’s important to evaluate the specific needs of your facility, as the right isolator can mitigate risks associated with electrical faults and improve the overall safety of your operations. In this exploration, we will guide you through the essential criteria to consider, helping you make an informed decision that not only meets regulatory standards but also aligns with your operational goals. Whether you are upgrading existing infrastructure or embarking on new installations, the right isolator selection will play a vital role in the long-term success of your electrical system.

High voltage isolators are critical components in electrical systems, designed to ensure safety and reliability during maintenance and operation. These devices serve the primary function of disconnecting a portion of an electrical circuit to prevent accidental energization, protecting both personnel and equipment. Understanding the basic principles of high voltage isolators is essential for selecting the appropriate model for your system. They typically consist of a switch mechanism that opens or closes the circuit and are engineered to handle the high stress associated with elevated voltages.
When choosing a high voltage isolator, one must consider various factors, including the voltage ratings, current carrying capacity, and environmental conditions in which the device will operate. High voltage isolators come in several types, such as manual or motor-operated, and are designed for different applications, from power generation to distribution systems.
It is vital to ensure that the isolator's specifications align with your system's operational conditions to maintain efficiency and longevity while minimizing the risk of failure or hazards during energy servicing operations. Additionally, factors such as installation space, maintenance requirements, and compliance with relevant safety standards play a pivotal role in the decision-making process.
When selecting the right high voltage isolators for an electrical system, it's crucial to understand the different types available and their specific applications. High voltage isolators are primarily classified into two categories: mechanical and digital isolators. Mechanical isolators, such as isolating switches, provide a physical interruption in the circuit, commonly used in substations to ensure safety during maintenance. They can handle high operational currents and are designed with robust insulation systems to withstand extreme voltage levels. According to industry data from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), mechanical isolators are essential for systems exceeding 1 kV, demonstrating their reliability in high-stress environments.
On the other hand, digital isolators have become increasingly popular, particularly with the rise of smart grid technologies. These isolators utilize semiconductor technology to maintain signal integrity without a direct electrical connection. Digital isolators are favored in applications requiring communication between high voltage and low voltage systems, as they provide enhanced noise immunity and faster switching speeds. A report from the IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference indicates that digital isolators can achieve isolation voltages above 5 kV, making them ideal for modern high voltage applications where precision and safety are paramount. Understanding these key differences is essential for ensuring the appropriate isolator is chosen to meet specific operational demands.
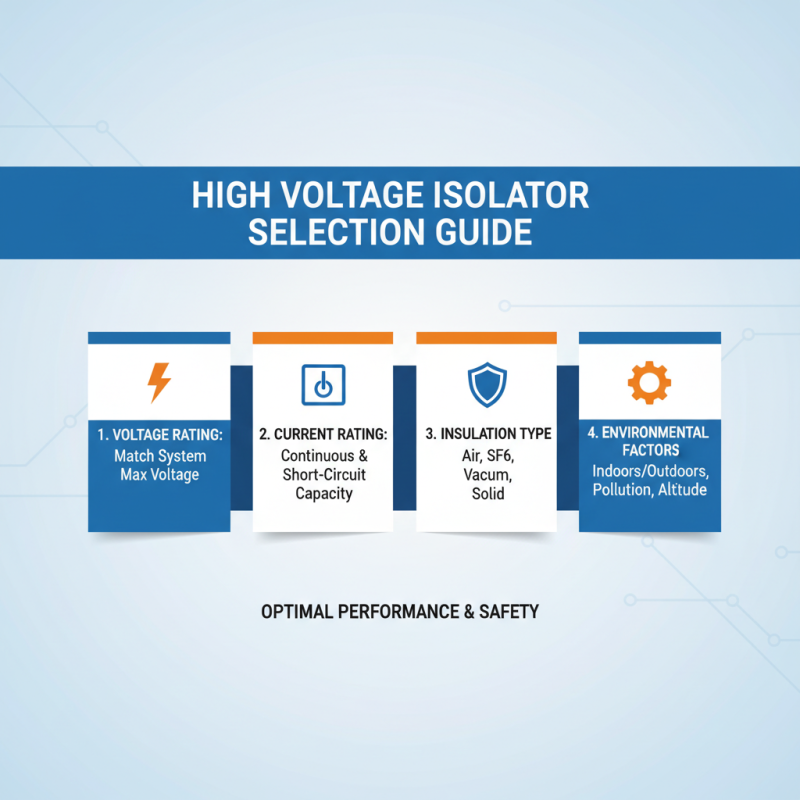
When selecting a high voltage isolator for your electrical system, several key factors must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and safety. First and foremost, assess the voltage rating of your system. High voltage isolators are designed for different voltage levels, and using one that isn’t appropriately rated can lead to insulation failure or pose safety hazards. Make sure to choose an isolator that meets or exceeds the maximum voltage your system will handle.
Additionally, consider the environmental conditions your isolator will be exposed to. Factors such as humidity, temperature extremes, and potential exposure to corrosive substances can significantly impact the longevity and functionality of the isolator. For outdoor applications, opt for units that are weatherproof and can withstand harsh conditions.
**Tips:** Regular maintenance checks on your isolation equipment can help identify potential issues before they escalate. Moreover, understand the physical space where the isolator will be installed; this includes ensuring that enough clearance is available for safe operation and maintenance.
Lastly, pay attention to the required switching frequency of the isolator. Different applications may necessitate varying cycle times – whether it's for routine maintenance or emergency situations. A high-frequency switch may offer better responsiveness in dynamic systems, while a standard isolator may suffice for more stable environments. Ensuring that the isolator aligns with your operational needs will enhance the reliability of your electrical system.
When installing high voltage isolators, safety and precision are paramount. Start by ensuring that the work area is properly de-energized and that all necessary personal protective equipment (PPE) is worn. Proper installation requires adherence to manufacturer specifications and industry standards. It is essential to verify that the isolators are suitable for the voltage levels and environmental conditions of your electrical system. Ensure that connections are secure, and consider employing qualified personnel for installation to minimize risks of errors.
Maintenance of high voltage isolators is critical for ensuring their reliable operation. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear and tear, corrosion, or any physical damage. Schedule routine maintenance checks to clean, lubricate, and tighten connections as needed. Testing the performance of the isolators periodically can help identify potential issues before they lead to failure. Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities can also aid in tracking the performance and lifespan of the equipment.
Implementing these practices will help extend the life of your isolators and improve the overall safety and efficiency of your electrical system.
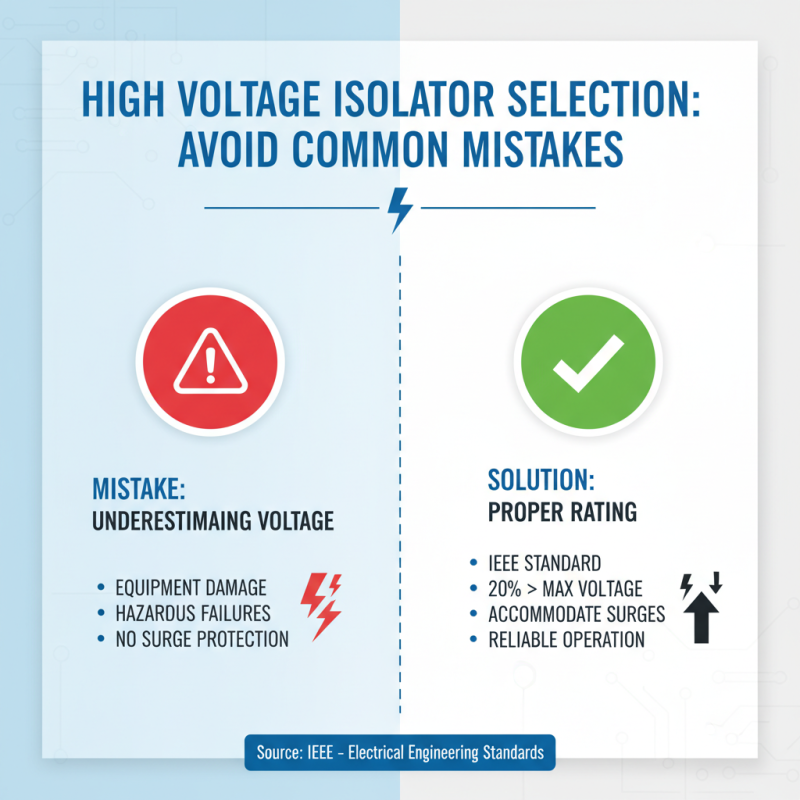
When selecting high voltage isolators for electrical systems, avoiding common mistakes is crucial to ensure both safety and efficiency. One prevalent error is underestimating the voltage ratings required for the specific application. According to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), isolators should be rated at least 20% higher than the maximum voltage anticipated in the system to accommodate potential surges and ensure reliable operation. Failing to account for these surges can result in equipment damage or hazardous failures.
Another frequent pitfall is neglecting the environmental factors that the isolator will be exposed to. The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) emphasizes that isolators must be chosen based on the ambient conditions, such as temperature variations, humidity, and exposure to corrosive elements. For instance, isolators installed in coastal areas or industrial settings may require special coatings or materials to prevent corrosion, which could compromise their performance. Adequately assessing these conditions is vital to prevent premature deterioration and costly replacements down the line.
Overlooking maintenance requirements is yet another mistake. A study from the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) highlighted that regular inspection and maintenance can extend the lifespan of isolators by up to 30%. Selecting isolators that allow easy access for maintenance ensures that performance can be routinely checked, and potential issues can be addressed before they escalate into serious failures. Understanding these factors can significantly enhance the safety and reliability of high voltage electrical systems.





