
Leave Your Message

The world of electrical insulation is vast and intricate, with a special focus on Glass Insulator 100b types. Renowned expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading authority in electrical engineering, states, “Understanding the different types of glass insulators is crucial for optimal performance.” This insight resonates deeply within industries that rely on dependable insulation.
Glass Insulator 100b types have various applications, from telecommunications to power transmission. Each type serves a specific purpose, ensuring safety and efficiency. For example, high-quality glass insulators are vital in maintaining the stability of electrical infrastructure. However, selecting the right type can often feel overwhelming due to numerous factors to consider.
It's important to recognize that not all glass insulators perform equally. Users may face challenges in identifying the best fit for their needs. Some insulators may not provide the durability expected, leading to unexpected issues. Reflecting on these nuances can lead to better decisions and ultimately enhance operational efficacy in the industry.

Glass insulators have long been essential in electrical systems. The 100b variants are particularly interesting. They come in various shapes and colors. Each type serves a unique purpose in different settings.
For example, the pin type insulator is commonly used on utility poles. It's designed to secure wires and prevent electrical leakage. Another common type is the suspension insulator, which hangs from a support structure. This design helps to carry high voltage lines over long distances. Each design reflects a specific engineering challenge, and balancing aesthetics with functionality can be tricky.
Color also plays a role. Clear glass insulators help blend into the environment. Meanwhile, dark or colored glass can be more visually appealing. However, the choice of color can complicate visibility during maintenance. It's an interesting contradiction. The variety in shapes and colors often leads to choices that are not always straightforward. Selecting the right insulator involves weighing multiple factors. It’s easy to overlook details that could impact performance. So, choosing the best glass insulator requires careful consideration and some trial and error.
| Type | Material | Color | Use Case | Voltage Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insulator Type A | Soda-Lime Glass | Clear | Distribution Lines | 25 kV |
| Insulator Type B | Lead Glass | Green | Telecommunication | 50 kV |
| Insulator Type C | Borosilicate Glass | Amber | High Voltage Lines | 110 kV |
| Insulator Type D | Aluminosilicate Glass | Blue | Substation Applications | 220 kV |
| Insulator Type E | Synthetic Glass Composite | Light Green | Renewable Energy Systems | 150 kV |
Glass insulators have a rich history that dates back to the late 19th century. Used primarily in electrical systems, these insulators played a crucial role in transmission lines. Early designs were simple and utilitarian. As the years progressed, aesthetics became more important. Craftsmen began to create colorful and uniquely shaped insulators.
In the 1920s and 1930s, the production of glass insulators became more standardized. Manufacturers improved the strength and durability of their products. Yet, many insulators from this era exhibit small imperfections. It's a reminder that craftsmanship often involves trial and error. Collectors appreciate such flaws as they add character.
Tips: When choosing glass insulators, consider both function and aesthetic appeal. Look for unique designs that resonate with you. Remember, imperfections can enhance the story behind each piece. They reflect their journey through time.
Glass insulators play a crucial role in the electrical industry. The 100b types are particularly notable for their durability and performance. These insulators are designed to withstand high voltage while minimizing electrical leakage. They feature a unique composition that provides both mechanical strength and resistance to environmental factors. This makes them ideal for outdoor installations, especially in harsh weather conditions.
Key specifications of the 100b glass insulators focus on insulation resistance and dielectric strength. These insulators typically have a high dielectric strength, ensuring they can handle voltage spikes without failure. Their insulation resistance often exceeds standard requirements, which is necessary for safe operation. Some may worry about their vulnerability to physical impacts. However, when installed correctly, they provide reliable service for many years.
In terms of performance metrics, the 100b glass insulators exhibit excellent thermal stability. They can function effectively in extreme temperatures. The aging process may affect some properties, leading to reduced effectiveness. Regular inspection is essential for maintaining their reliability. While some users may overlook this aspect, it is crucial for long-term performance in any electrical setup.
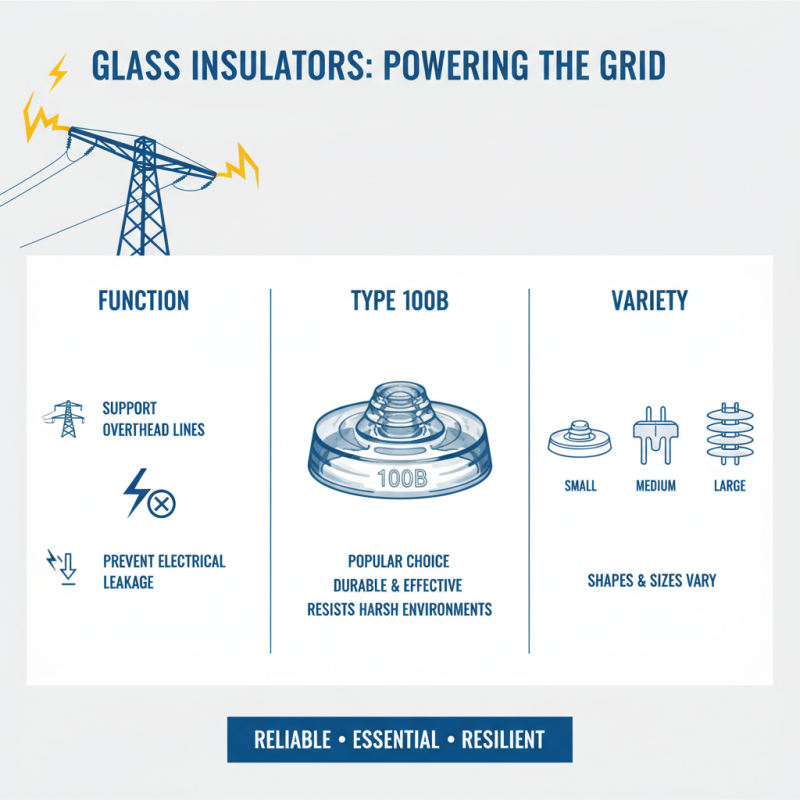
Glass insulators play a vital role in electrical systems. They are crucial for supporting overhead power lines while preventing electrical leakage. They come in various shapes and sizes. The 100b type is particularly popular due to its durability and effectiveness. These insulators can withstand harsh environments.
Commonly, glass insulators are used in transmission lines. They ensure that electricity travels safely across long distances. Their transparent surface allows light to penetrate, which helps keep them clean from dirt and pollutants. In substations, they help connect different electrical components securely. They also feature in telecommunications, keeping lines stable and protected.
However, not all glass insulators are perfect. Some may not maintain insulation over time, creating potential hazards. Users should regularly inspect them for cracks or defects. Understanding the specific environment is essential for optimal performance. Each application requires careful consideration of the insulator type. Users may have to rethink their choices based on local conditions and long-term reliability.
Proper installation and maintenance of glass insulators are crucial for their effectiveness. Start by ensuring that the insulator is free from cracks and dirt. A clean surface enhances electrical performance. Always use the right tools during installation. Improper tools can lead to damage. Remember that positioning matters. Insulators should be placed at appropriate heights to avoid environmental wear.
Regular inspections help catch issues early. Look for signs of wear, including scratches and moisture. Adjustments may be needed to stabilize the installation. If an insulator shows excessive wear, consider replacing it. A proactive approach extends the insulator's lifespan. Neglect can lead to failures, impacting overall system reliability.
User feedback often highlights common installation mistakes. Some forget to secure the insulator properly. Others overlook the impact of external factors, like weather. Understanding these pitfalls can enhance maintenance strategies. Educating users about these nuances is essential. Encourage attention to detail to ensure longevity and safety in all setups.





